Attention! These 13 batches of food failed the sampling inspection!
According to the WeChat official account message of "City Talk" WeChat, processed grain products, edible agricultural products, sugar, tea and related products, dairy products, beverages, alcohol, cakes, roasted seeds and nuts and nut products … … Are these foods that we often eat safe? Recently, the General Administration of Market Supervision organized food safety supervision and sampling inspection.
This sampling inspection includes processed grain products, edible agricultural products, sugar, tea and related products, dairy products, beverages, alcohol, cakes, roasted seeds and nuts, biscuits, starch and starch products, convenience foods, potatoes and puffed foods, egg products, bean products, bee products, vegetable products, fruit products, meat products, aquatic products, condiments, frozen drinks, quick-frozen foods, candy products and so on.
one
650 batches of 27 categories of food samples:
● 13 batches of 7 categories of food, including processed food, dairy products, cakes, convenience foods, potatoes and puffed foods, fruit products and infant formula foods, were unqualified.
● The main problems found are microbial pollution, excessive use of food additives, substandard quality indicators, and inconsistency between quality indicators and labeling values.
2
Unqualified food found in sampling inspection:
● The General Administration of Market Supervision has instructed provincial-level market supervision departments such as Jilin, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Shandong, Hubei, Hunan, Guangdong, Guangxi and Shaanxi to immediately organize verification and disposal, find out the product flow, and urge enterprises to take measures such as recalling unqualified products from the shelves to control risks; Strictly deal with violations of laws and regulations according to law; Timely disclose the risk prevention and control measures and verification and disposal of enterprises to the public, and report to the General Administration.
Specific situation
I. Microbial pollution
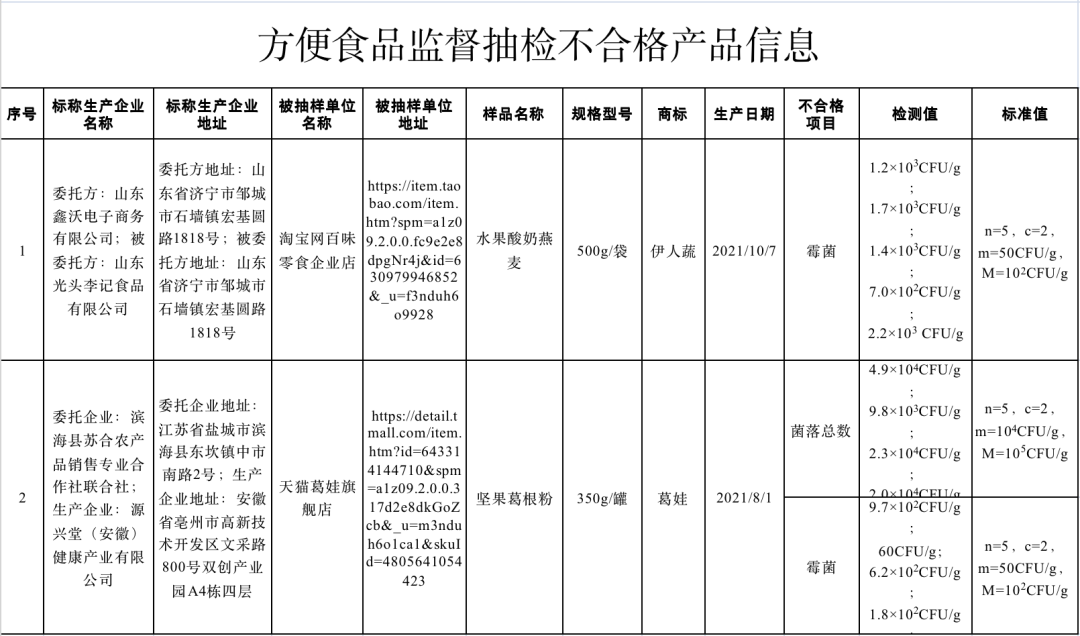
(1) The fruit yogurt oats sold by Taobao Baiwei Snacks Enterprise Store (operated by Zoucheng Baiwei E-Commerce Co., Ltd., Jining City, Shandong Province) and commissioned by Shandong Xinwo E-Commerce Co., Ltd. to produce by Shandong Guangtou Li Ji Food Co., Ltd., in which the number of molds does not meet the national food safety standards.
(II) Nut kudzu root powder sold by Tmall Gewa flagship store (operator is Hubei Gewa Food Co., Ltd.) in Tmall Mall (online shop) and nominally produced by Yuanxingtang (Anhui) Health Industry Co., Ltd. entrusted by Suhe Agricultural Products Sales Cooperative Association of Binhai County, Yancheng City, Jiangsu Province, in which the total number of colonies and the number of molds do not meet the requirements of product implementation standards.
(3) Osmanthus Jelly sold by Manwu Department Store in Xiufeng District, Guilin City, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region and nominally produced by Guilin Valley Mill Food Co., Ltd., in which the number of Staphylococcus aureus and the total number of colonies do not meet the national food safety standards.
(4) Handmade glutinous rice blocks sold by Tmall Lvhui food franchise store (operator is Yuyao Lvhui International Trade Co., Ltd., Ningbo City, Zhejiang Province) in Tmall Mall (online store) and nominally produced by Hemudu Yuansheng Rice Cake Factory, Yuyao City, Ningbo City, Zhejiang Province, in which the total number of colonies does not meet the national food safety standards.
(5) The Shuimo Rice Cake, which is sold by Taobao’s three-person snack shop (operated by lanshan district Qunbo Food Store in Linyi City, Shandong Province) and nominally produced by Haishu Zenghui Food Factory in Ningbo City, Zhejiang Province, in which the total number of colonies does not meet the national food safety standards.
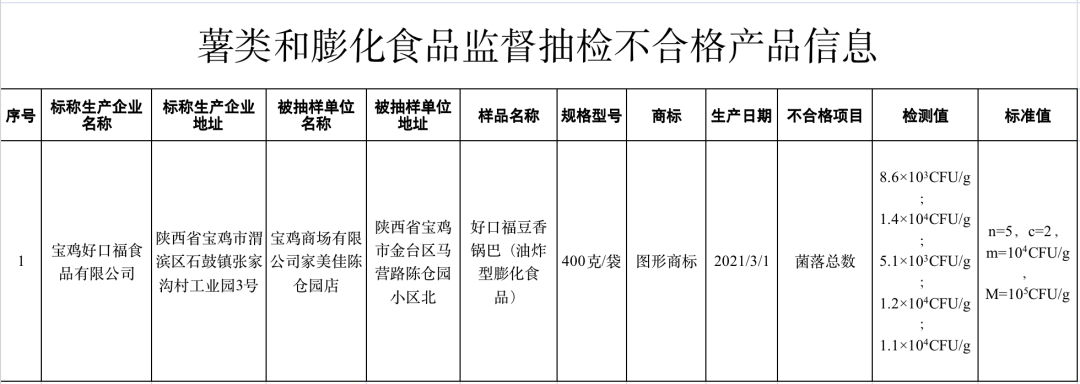
(VI) Haokoufu bean crispy rice (fried puffed food) sold by Jiameijia Chencang Garden Store of Shaanxi Baoji Shopping Mall Co., Ltd. and nominally manufactured by Shaanxi Baoji Haokoufu Food Co., Ltd., in which the total number of colonies does not meet the national food safety standards.
Second, the problem of out-of-range and over-limited use of food additives
(1) Chuncui infant formula (0— 0 & mdash; 0 & mdash; 0 & mdash; 0 & mdash; 0 & mdash; 0 & mdash; 0 & mdash; 0 & mdash; 0 & mdash; 6 months old, country of origin: Australia), in which the detection value of vanillin does not meet the national food safety standards. Changsha Aoyou Dairy (China) Co., Ltd. objected to the inspection results and applied for re-inspection; After re-inspection, the conclusion of initial inspection shall be maintained. The Market Supervision Bureau of Wangcheng District of Changsha City has urged Aoyou Dairy (China) Co., Ltd. to immediately recall and seal 6,726 cans of unqualified food, confiscate the illegal income of 20,300 yuan and impose a fine of 9,621,300 yuan. Ningbo Yinzhou District Market Supervision Bureau confiscated illegal income and imposed a total fine of 11,500 yuan on the mother-baby products store of Mommy Garden in Jison, Yinzhou, Ningbo, which sold unqualified products.
(2) Tianshan Mume, which is sold by Pinduoduo Dixiangwei Food Franchise Store (operated by Guangdong Guangzhou Dixiangwei Food Co., Ltd.) in Pinduoduo (mobile APP) and nominally produced by Kaishili Food Factory in Jiexi County, Jieyang City, Guangdong Province, and the detected values such as the sum of the respective dosages of brilliant blue, amaranth and colorants of the same color in the mixed use of them in the maximum dosage ratio do not meet the national food safety standards.
(3) The ebony sold by Pinduoduo Lexiangxiong official flagship store (operated by Shandong Weifang Qiqi E-Commerce Co., Ltd.) in Pinduoduo (mobile phone APP) and nominally commissioned by Shandong Weifang Qiqi E-Commerce Co., Ltd. to produce by Liaoning Huludao Xingcheng Hongfa Food Co., Ltd., among which the detected values such as the sum of the respective dosages of brilliant blue, carmine and colorants of the same color in the mixed use ratio of their maximum dosages do not meet the national food safety standards.
(4) Tianshan Mume, which is sold in Pinduoduo (mobile APP) by Pinduoduo’s official flagship store of five seasons food (operated by Guangdong Jieyang Duobaoyu E-commerce Co., Ltd.) and commissioned by Guangdong Jieyang Jiexi Fifth Season Food Co., Ltd. to produce by Shuangmao Food Factory in Jiexi County, Guangdong Province, in which the detection values of bright blue and amaranth do not meet the national food safety standards.
(5) Buckwheat cold noodles sold by Tmall Juzhen Huipin Flagship Store (operated by Jilin Juzhen Food Development Co., Ltd.) in Tmall Mall (online store) and produced by Jilin Juzhen Huipin Trading Co., Ltd. and meihekou city Meihechun Food Co., Ltd. in Tonghua City, Jilin Province, in which the detection values of sorbic acid and its potassium salt (calculated by sorbic acid), dehydroacetic acid and its sodium salt (calculated by dehydroacetic acid) do not meet the national food safety standards.
Third, the quality index is not up to standard
The spicy stone cakes (cakes) sold by Taobao Qin Restaurant (the operator is pucheng county Qin Restaurant Specialty Store in Weinan City, Shaanxi Province) and nominally produced by Shaanxi Maonv Food Co., Ltd., in which the peroxide value (measured by fat) does not meet the national food safety standards.
Fourth, the quality index does not match the label value.
The high calcium buffalo milk sold by Guangxi Guanye Investment Development Co., Ltd. Nanning Anji Wanda Store and produced by Guangxi Shibu Dairy Co., Ltd. entrusted by Guangxi Yangli Food Co., Ltd. met the national food safety standards, but did not meet the product labeling requirements. Guangxi Shibu Dairy Co., Ltd. objected to the inspection results and applied for re-inspection; After re-inspection, the conclusion of initial inspection shall be maintained.
Annex 1
Small knowledge of some unqualified inspection items
First, mold
Mold is an indicative index to evaluate the quality of food hygiene. The number of molds in food refers to the number of mold colonies formed in 1g or 1mL of food samples after being treated and cultured under certain conditions. If the mold in food exceeds the standard seriously, it will destroy the nutritional components of food, make food lose its edible value, and may also produce mycotoxin; Long-term consumption of food with excessive mold may endanger human health. National Food Safety Standard for Blending Cereal Products (GB 19640— In 2016), it is stipulated that the mold test results of five samples of the same batch of brewed cereal products should not exceed 102CFU/g, and the test results of two samples are allowed to exceed 50CFU/g at most. Convenient Blended Products (Q/AYXT 0004S— 2021) stipulates that the test results of mold in five samples of the same batch of products for convenient preparation shall not exceed 102CFU/g, and the test results of two samples are allowed to exceed 50CFU/g at most. The reason why the number of molds in brewed cereal products and instant brewed products exceeds the standard may be that the raw materials or packaging materials are contaminated by molds, or that the sanitary conditions of the products are not well controlled during production and processing, or that the storage and transportation conditions of the products are improper.
Second, the total number of colonies
The total number of colonies is an indicative microbial index, not a pathogen index, which reflects the hygienic status of food in the production process. If the total number of colonies in food seriously exceeds the standard, it will destroy the nutritional components of food and make food lose its edible value; It will also accelerate the deterioration of food, which may endanger human health. Convenient Blended Products (Q/AYXT 0004S— 2021) stipulates that the detection results of the total number of colonies of five samples of the same batch of products for convenient preparation shall not exceed 105CFU/g, and the detection results of two samples are allowed to exceed 104CFU/g at most. National Food Safety Standards for Pastry and Bread (GB 7099— 2015) stipulates that the total number of colonies of five samples of the same batch of pastry food products should not exceed 105CFU/g, and the detection results of two samples are allowed to exceed 104 cfu/g at most; "rice cake" (SB/T 10507— In 2008), it was stipulated that the microbial index of Shuimo rice cake should meet the national food safety standard "Quick-frozen noodle rice products" (GB 19295— "Cooked food" in 2011), that is, the test results of the total number of colonies of five samples of the same batch of products shall not exceed 105CFU/g, and the test results of one sample are allowed to exceed 104 cfu/g at most; National Food Safety Standard Puffed Food (GB 17401— 2014)It is stipulated that the total number of colonies of five samples of puffed food in the same batch should not exceed 105CFU/g, and the detection results of two samples are allowed to exceed 104CFU/g at most. The reason why the total number of colonies in instant concocted products, cakes, rice cakes and puffed food exceeds the standard may be that the enterprise has not strictly controlled the sanitary conditions in the production and processing process as required, or it may be related to the lax packaging and sealing of the products or improper storage and transportation conditions.
Third, Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus is a common pathogen. Once food is not properly preserved, Staphylococcus aureus can multiply in large numbers. Eating food seriously contaminated by Staphylococcus aureus may cause food poisoning, resulting in severe vomiting, fever, diarrhea and other symptoms. Limit of pathogenic bacteria in food according to the national standard of food safety (GB 29921— In 2013), the detection results of Staphylococcus aureus in five samples of the same batch of pastry food products should not exceed 103CFU/g, and the detection results of one sample should exceed 102CFU/g at most. The reason why the number of Staphylococcus aureus in cakes exceeds the standard may be that the production and processing personnel carry bacteria and cause pollution; It may also be raw material pollution, improper control of sanitary conditions in the production process, incomplete sterilization and cross-contamination of products; It may also be related to improper storage and transportation of products.
Iv. Vanillin
Vanillin is a commonly used food additive. Because of its vanilla bean aroma and rich milk aroma, it is widely used in all kinds of flavored foods that need to increase milk aroma, especially dairy products, baked goods, beverages and edible oil. Using vanillin according to the standard requirements will not do harm to human health, but a large intake of vanillin will lead to dizziness, nausea and other symptoms, and in severe cases, it will cause liver and kidney damage. National Standard for Food Safety-Standard for the Use of Food Additives (GB 2760— In 2014), it is stipulated that no edible spices should be added to infant formula food from 0 to 6 months, and vanillin can be used in limited amounts for older infants and young children’s formula food according to regulations. The reason for the detection of vanillin in the first stage of infant formula milk powder may be that the company did not completely clear the scene when switching the food production lines for infants of different months; It may also be that illegal traders illegally add such substances in order to achieve the purpose of shoddy and fake.
Five, bright blue
Brilliant Blue, also known as Edible Blue No.2, is a water-soluble non-azo compound, which is a common synthetic colorant and widely used in food production. If the food with excessive bright blue is ingested for a long time, it may be teratogenic and carcinogenic. National Standard for Food Safety-Standard for the Use of Food Additives (GB 2760— In 2014), the maximum dosage of brilliant blue in preserved fruits was 0.025g/kg. The detection value of bright blue in preserved fruits exceeds the standard value, which may be caused by inaccurate measurement in the production process, excessive use by production enterprises to improve the color and market value of products, or adulteration and fraud by enterprises.
Six, amaranth red
Amaranth red, also known as blue acid red and azo compounds, is a common synthetic colorant and widely used in food production. If the food with amaranth exceeding the standard is ingested for a long time, it may be teratogenic and carcinogenic. National Standard for Food Safety-Standard for the Use of Food Additives (GB 2760— In 2014), the maximum dosage of amaranth in preserved fruits was 0.05g/kg. The reason why the detection value of amaranth in candied preserved fruits exceeds the standard value may be that the production enterprises overuse it to improve the color and market value of the products, or that the enterprises adulterate and falsify the pigments.
Seven, the same color colorants when mixed use of their respective dosage of the proportion of the sum of the maximum amount.
Colorants, also known as food pigments, are used to give and improve the color of food. If it is taken excessively for a long time, it will increase the burden on the liver and gastrointestinal tract and cause certain harm to human health. National Standard for Food Safety-Standard for the Use of Food Additives (GB 2760— In 2014), it is stipulated that the sum of the ratio of the respective dosage to the maximum dosage of colorants with the same color should not exceed 1. The reason why the sum of the ratio of the respective amounts of colorants with the same color in candied fruit to the maximum amount exceeds the standard value may be that the production enterprises do not understand the national food safety standards and add more colorants with the same color in excess, or that the amount of colorants with the same color is not strictly controlled in the production and processing process.
Eight, carmine
Carmine, also known as scarlet, brilliant scarlet and azo compounds, is a common synthetic colorant and widely used in food production. There is no poisoning phenomenon of carmine in animal experiments, but if the food with carmine exceeding the standard is ingested for a long time, it may be teratogenic and carcinogenic. National Standard for Food Safety-Standard for the Use of Food Additives (GB 2760— In 2014), the maximum dosage of carmine in preserved fruits was 0.05g/kg. The reason why the detection value of carmine in preserved fruit exceeds the standard value may be that the final product carmine exceeds the standard due to inaccurate measurement in the production process, or that the production enterprise overuses it to improve the color and market value of the product, or that the enterprise adulterates and falsifies and abuses the pigment.
Nine, sorbic acid and its potassium salt (in sorbic acid)
Sorbic acid and its potassium salt have strong antibacterial activity and good antiseptic effect, and are widely used as food preservatives at present. Long-term consumption of foods with excessive sorbic acid and its potassium salt may cause harm to the growth of liver, kidney and bone. National Standard for Food Safety-Standard for the Use of Food Additives (GB 2760— 2014) stipulates that sorbic acid and its potassium salt (calculated by sorbic acid) shall not be used in other grain flour products. The reason why sorbic acid and its potassium salt (calculated by sorbic acid) were detected in buckwheat cold noodles may be that enterprises used it beyond the scope in order to extend the shelf life of the products or make up for the poor sanitary conditions in the production process.
X. dehydroacetic acid and its sodium salt (in dehydroacetic acid)
Dehydroacetic acid and its sodium salt, as a broad-spectrum food preservative, have strong inhibition ability to mold and yeast. Dehydroacetic acid and its sodium salt can be completely absorbed by human body, and can inhibit various oxidases in human body. Excessive intake of dehydroacetic acid and its sodium salt for a long time will be harmful to human health. National Standard for Food Safety-Standard for the Use of Food Additives (GB 2760— In 2014), dehydroacetic acid and its sodium salt are not allowed to be used in other grain flour products. The reason why dehydroacetic acid and its sodium salt (calculated by dehydroacetic acid) were detected in buckwheat cold noodles may be that enterprises used it beyond the scope in order to extend the shelf life of the products or make up for the poor sanitary conditions in the production process.
XI. Peroxide value (in terms of fat)
Peroxide value is an early indicator of oil rancidity, which mainly reflects the degree of oil oxidation. Eating foods with excessive peroxide value will generally not cause harm to human health, but long-term consumption of foods with excessive peroxide value may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort and diarrhea. National Food Safety Standards for Pastry and Bread (GB 7099— 2015) stipulates that the maximum limit value of peroxide value (in terms of fat) in cakes is 0.25 g/100 g. The reason why the peroxide value (measured by fat) in cakes exceeds the standard value may be that the fat in raw materials has been oxidized, or it may be related to improper control of environmental conditions during storage and transportation.
XII. protein
Protein is a macromolecular organic compound with amino acids linked together by peptide bonds and forming a certain spatial structure. Protein is an important component of tissues and organs, a component of many important physiological active substances, and can also supply energy. National Food Safety Standard modified milk (GB 25191— In 2010), the protein content in modified milk should be ≥ 2.3 g/100g, and the product packaging label clearly States "high quality milk protein ≥ 3.7g/100mL ",after the unit conversion of test results, the test value of protein in this batch of products meets the national food safety standards, but it does not meet the express quality requirements of the products. The reason why the content of protein in dairy products is not up to standard may be that the quality control of raw and auxiliary materials is not strict, or that the enterprise fails to organize production according to the label or the requirements of enterprise standards.
Annex 2